Breast Engorgement: All You Need To Know
Breast engorgement is a common condition that is still preventable. It is important to be aware of the fullness in the breasts and empty them continuously.
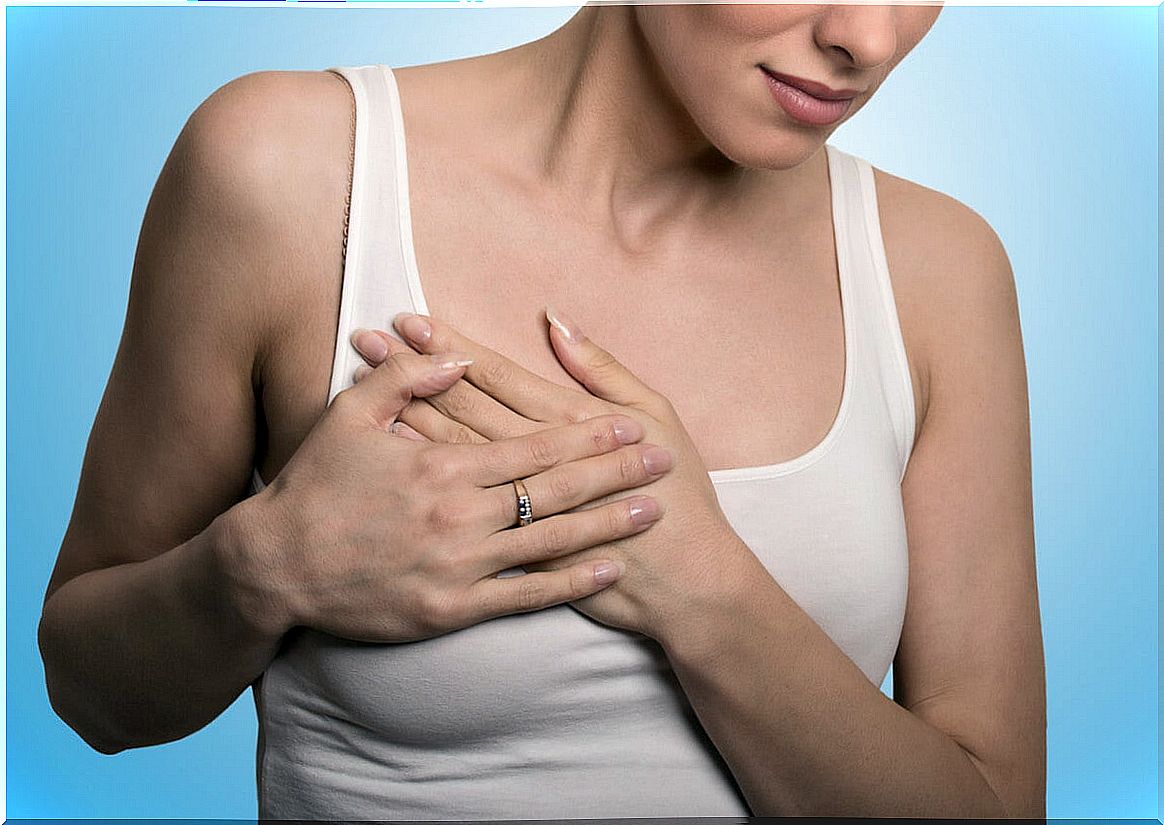
Breast engorgement is a condition in which there is an excessive accumulation of milk in mothers who are breastfeeding. The main characteristic is that the breasts feel hard and sore.
Before engorgement, the breasts feel swollen, tender, and heavy when the milk comes in. This is called fullness of the breast . If it persists and increases, the disorder occurs. The process usually begins within three to five days after delivery.
The risk of engorgement is that, if it progresses, it can turn into a disease called mastitis . It occurs because there is too much milk, it is not expressed frequently, or the mother is not breastfeeding.
Causes of breast engorgement
In the days after delivery there is an increase in blood flow in the breasts. This helps the breasts produce more milk, but it also causes pain and discomfort.
The usual thing is that first there is fullness of the breast and then engorgement develops. Although it is common for it to occur in the first few weeks after delivery, it could also occur at any time during breastfeeding.
The main reasons for this to happen are the following:
- There is an overabundant milk production.
- Not enough milk expression.
- One feed of the baby is skipped.
- There is difficulty for the baby to suck.
- Weaning occurs too quickly or there is no lactation.
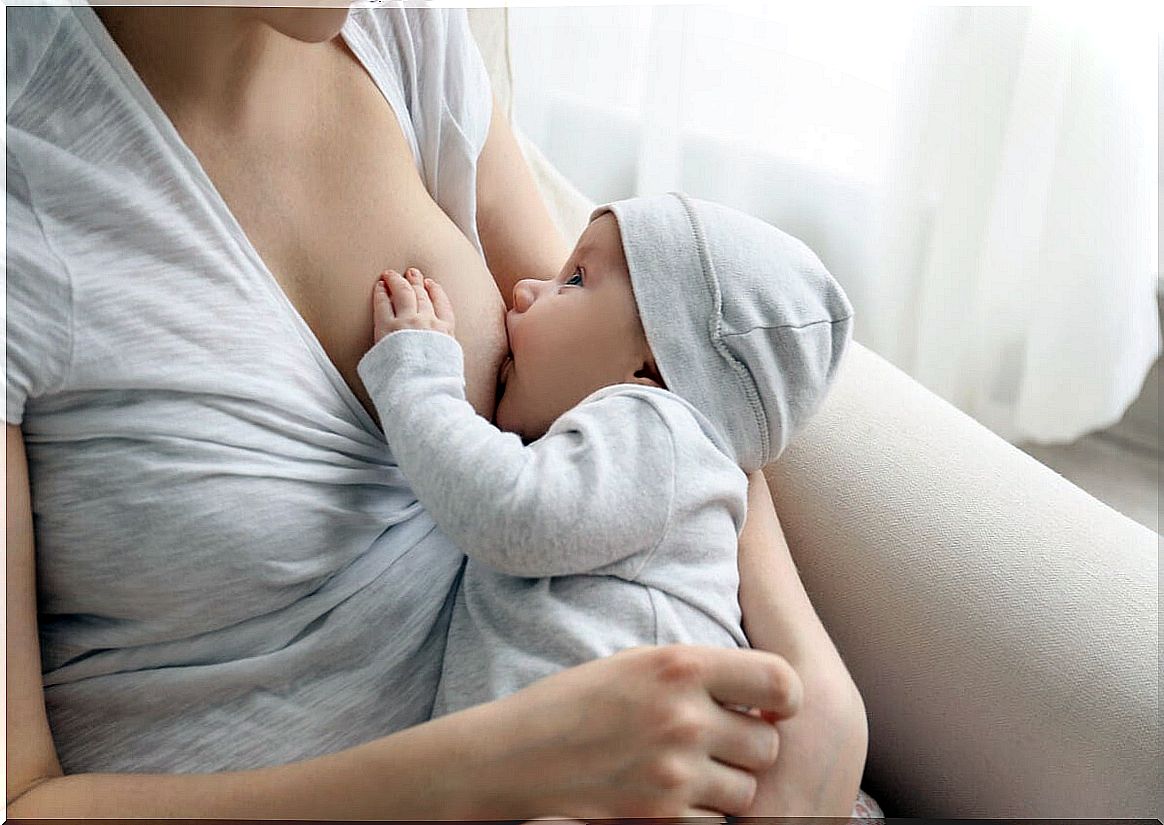

Symptoms of engorgement
The most obvious symptom of engorgement is breast swelling. Sometimes this only happens in one of them and other times in both. In some women the swelling extends to the chest or armpits.
Other common symptoms are the following:
- Feeling of hardness or tightness in the breast.
- Heaviness or fullness in the breasts.
- The skin feels tight.
- The breast feels warm.
Some women also experience mild fever and fatigue during the first few days of breastfeeding. This condition is known as milk fever and it usually remits spontaneously. Fever is not a reason to stop breastfeeding.
Either way, the elevated temperature is a reason for medical consultation. It is important to rule out a possible infection, as this can aggravate the evolution.
How can it be treated?
The treatment to be followed depends on whether the mother is breastfeeding or not. In the first case, the most appropriate measures are the following:
- Preparing the breasts before breastfeeding: the goal is to soften them. For this you can use a warm water compress applied for a couple of minutes. Hand massages or breast pumps are also used.
- Increase the frequency of breastfeeding: in addition to completely emptying the breasts after the baby eats.
- Go to some drugs: it should be done under medical supervision. It is advisable to use an analgesic and anti-inflammatory, always with the corresponding indications.
- Cold compresses: If none of the above measures work, it is a good idea to apply a cold or ice compress for 15 minutes, every hour.
In case the mother is not breastfeeding, the appropriate measures are the following:
- Moderate the expression of milk: you should not use the breast pump too often.
- Cold compresses: apply once an hour for 15 minutes, protecting the skin with a cloth.
- Drugs: the doctor will indicate the drugs to use to reduce pain and inflammation. They are generally over the counter.
- Support for the breasts: A suitable bra must be used.

How can it be prevented?
The best way to prevent engorgement is by expressing your milk regularly. This is accomplished when the baby is fed or through the use of the breast pump. What to keep in mind is the following:
- Breastfeeding the baby: it should be done every time he shows that he has an appetite.
- Use proper technique: the baby must latch on well for the suction to be effective.
- Empty the breasts: after the baby feeds it is necessary to empty the breast completely. This also applies when the baby is switched from one breast to the other.
It is a good idea to prepare the breasts before feeding the baby, especially if they are very hard. Simply express a little milk. If the mother is not breastfeeding, she should use the breast pump as indicated in the previous section.
Ask if you have questions about the breastfeeding technique
Breast engorgement is more common in the first weeks after delivery. It is important to be vigilant in this first phase to prevent, as much as possible, this annoying condition.
If there are doubts about how to feed the baby, it is best that the medical staff offer appropriate guidance. In the event that breast engorgement occurs and does not disappear or is accompanied by other symptoms, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible.